Extracorporeal Life Support (ECLS)
= 에크모, 체외막산소화장치 (ECMO, Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation)
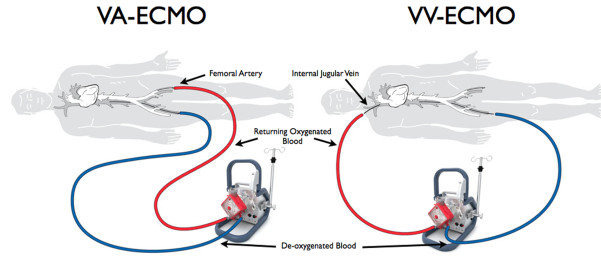
Respiratory ECLS or Veno-Venous (VV) ECLS
Venous blood (>1.5L/min) is aspirated from the vena cava or RA, passes through the pump and oxygenator and is then pumped back to the RA. VV ECLS provides support for severe respiratory failure, there is no direct cardiac support with VV ECLS. VA ECLS can also be used for primary respiratory failure in patients with some degree of concomitant cardiac failure.
정맥혈(분당 1.5리터 이상)이 대정맥 또는 우심방(RA)에서 흡입되어 펌프와 산소화기를 통과한 후 다시 우심방으로 주입됩니다. VV ECLS(정맥-정맥 체외생명유지장치)는 중증 호흡부전을 지원하지만, VV ECLS 자체는 심장을 직접적으로 지원하지 않습니다. VA ECLS(정맥-동맥 체외생명유지장치)는 일부 심장 기능 저하가 동반된 환자에서 일차적 호흡부전을 치료할 때에도 사용할 수 있습니다.
Respiratory or VV ECLS
VV ECLS is indicated in patients with potentially reversible, acute severe lung failure who continue to deteriorate despite optimal conventional support such as ‘lung protective’ mechanical ventilation (low tidal volumes, limited plateau pressures [Pplat]) or other advanced therapies (prone position, inhaled pulmonary vasodilators, high frequency oscillation). ECLS should be considered before refractory lung failure or multi-organ failure develops.
VV ECLS는 ‘폐 보호’ 기계환기(저환기량, 제한된 폐플래토 압력)나 기타 고급 치료법(복위 자세, 흡입 폐혈관확장제, 고주파 진동 환기)과 같은 최적의 기존 치료에도 불구하고 상태가 계속 악화되는, 잠재적으로 가역적인 급성 중증 폐부전 환자에서 적응증이 됩니다. ECLS는 난치성 폐부전이나 다기관 부전이 발생하기 전에 고려되어야 합니다.
Pathologic conditions that may require VV ECLS:
– ARDS
– Severe Air Leak Syndrome
– Pulmonary contusion
– Inhalation Injuries (gastric contents, near drowning, smoke)
– Status asthmaticus
– Airway Obstruction
– Bridge to lung transplantation
– Acute graft failure following lung transplant
– Alveolar proteinosis
Standard criteria for starting VV ECLS:
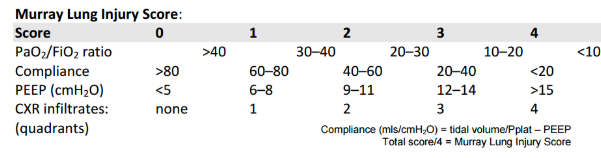
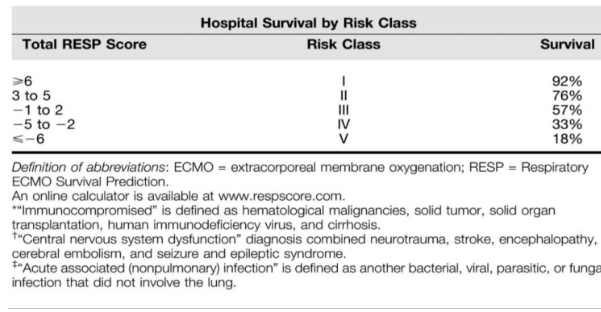
1. Murray score >3 (see below)
2. Hypoxaemia: PaO2/FiO2 <10 on FiO2 0.9 or higher for >1 hr
3. Hypercapnia: PaCO2 >11 or pH <7.20 for >1 hr
4. Corrected Minute Ventilation: >10 L/min (surrogate marker of increased dead space: Min Ventilation x PaCO2/5.4)
5. Pplat >30cmH2O, in absence of high pleural pressures (e.g. abdominal distension)
6. Static Compliance of respiratory system: <20mls/cmH2O
7. Less than 7 days of high pressure mechanical ventilation
Contraindications for VV ECLS:
– Progressive non-recoverable lung disease, not amenable to lung transplantation
– Chronic severe pulmonary hypertension with right ventricular failure (consider VA ECLS)
– Severe cardiac failure / Cardiac arrest (consider VA ECLS)
– Advanced malignancy
– Chronic organ dysfunction
– Lung Failure associated with bone marrow transplantation
– Contraindication to anticoagulation therapy
– Recent spinal cord or central nervous system trauma or haemorrhage
– Mechanical ventilation with FiO2 >0.9 and Pplat >30 cmH2O for >7 days
– Age >70 yrs
– BMI >30, BMI < 5
– Trauma with multiple bleeding sites
– Significant immunosuppression
– Recent diagnosis of haematological malignancy
* RESP score (점수가 높을 수록 좋다.)
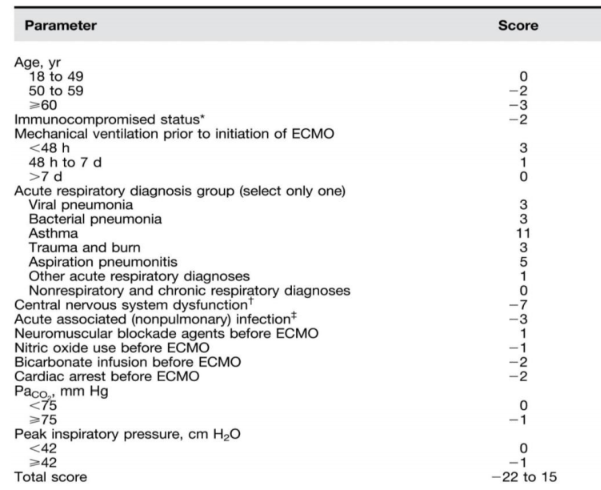
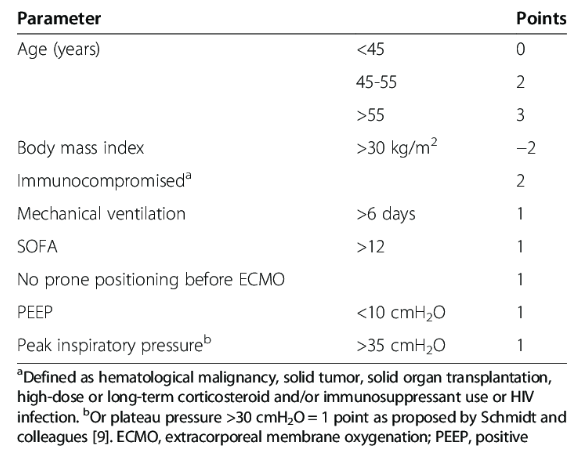
* PRESERVE score (점수가 높을 수록 좋지 않다.)
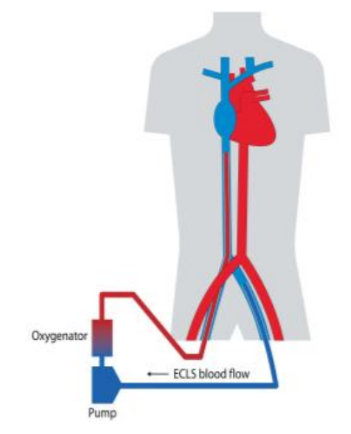
Cardiac ECLS or Veno-Arterial (VA) ECLS
Venous blood is aspirated from the vena cava or right atrium (RA), passes through the pump and oxygenator and is pumped back to the aorta. The return arterial cannula may be placed in a peripheral (femoral artery) or central (ascending aorta) location. VA ECLS provides support for severe cardiac failure (often with associated respiratory failure).
정맥혈은 대정맥 또는 우심방(RA)에서 흡입되어 펌프와 산소화기를 통과한 후 대동맥으로 주입됩니다. 환류 동맥 캐뉼라는 말초(대퇴동맥) 또는 중심(상행 대동맥) 위치에 삽입될 수 있습니다. VA ECLS는 중증 심부전(종종 호흡부전이 동반됨)을 지원하는 데 사용됩니다.
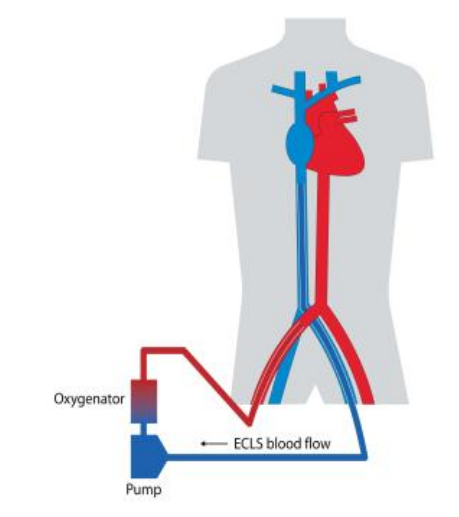
Cardiac or VA ECLS
Veno-arterial ECLS is used for short-term support in patients with severe heart (or heart and lung) failure where volume therapy, vasoactive medication and intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation have failed to provide adequate systemic perfusion. The decision to deploy VA ECLS is often made emergently in patients with acute circulatory shock not responding to conventional support therapies, cardiopulmonary resuscitation or not weaning from intraoperative cardiopulmonary bypass. If possible, the patient should be reviewed by Cardiology, Cardiothoracic Surgery and Critical Care Medicine prior to deployment of VA ECLS.
Indices of tissue hypoperfusion include systemic hypotension, mental status changes, oliguria, core-peripheral temperature gradient, skin mottling, myocardial ischaemia and
increased serum lactate concentration. In patients with satisfactory arterial oxygenation and haemoglobin concentration, inadequate systemic perfusion can be inferred by mixed venous oxygen saturation less than 70%.
정맥-동맥(VA) ECLS는 체액 요법, 혈관작용제 투여, 대동맥내풍선펌프(IABP) 사용에도 불구하고 충분한 전신 관류가 이루어지지 않는 중증 심부전(또는 심장·폐 부전) 환자에서 단기적인 지원을 위해 사용됩니다. VA ECLS 적용 여부는 종종 기존 치료에 반응하지 않는 급성 순환쇼크 환자, 심폐소생술이 필요한 환자, 혹은 수술 중 심폐우회술에서 이탈이 어려운 환자에서 긴급하게 결정됩니다. 가능하다면 VA ECLS 적용 전에 심장내과, 심장흉부외과, 중환자의학과에서 환자를 평가하는 것이 바람직합니다.
조직 저관류의 지표에는 전신 저혈압, 의식 변화, 핍뇨, 중심-말초 체온 차, 피부 반점, 심근 허혈, 혈중 젖산 농도 증가 등이 포함됩니다. 동맥 산소화와 혈색소 농도가 적절한 환자에서 전신 관류 부전은 혼합 정맥 산소포화도(MvO₂)가 70% 미만일 때 추정할 수 있습니다.
Pathologic conditions that may require VA ECLS:
– Post-cardiotomy cardiogenic shock
– Ischaemic cardiogenic shock
– Witnessed cardiac arrest (ECPR: extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation)
– Bridge to decision regarding suitability for therapy (e.g. revascularisation)
– Bridge to longer term support (e.g. Ventricular Assist Device [VAD], transplantation)
– Acute decompensation of Dilated Cardiomyopathy
– Acute fulminant myocarditis
– Massive pulmonary embolism
– Valvular heart disease
– Refractory arrhythmia’s (VT/VF)
– Massive haemoptysis / pulmonary haemorrhage
– Trauma (e.g. pulmonary / cardiac or major vessel)
– Sepsis with profound cardiac depression
– Overdose of cardiac depressant medication
– Acute graft failure after heart transplantation
– Anaphylactic shock
– Congenital cardiac anomalies
Contraindications for Cardiac ECLS:
– Progressive non-recoverable cardiac failure, not amenable to transplantation or VAD
– Severe aortic valve regurgitation
– Aortic dissection
– Un-witnessed cardiac arrest (risk of ischaemic hypoxic encephalopathy)
– Advanced malignancy
– Chronic organ dysfunction
– Contraindication to anticoagulation therapy
– Recent spinal cord or central nervous system trauma or haemorrhage
– Age >70 yrs (consider pre-morbid status)
– BMI >30, BMI <15
– Trauma with multiple bleeding sites
– Significant immunosuppression
– Recent diagnosis of haematological malignancy
* SAVE-score
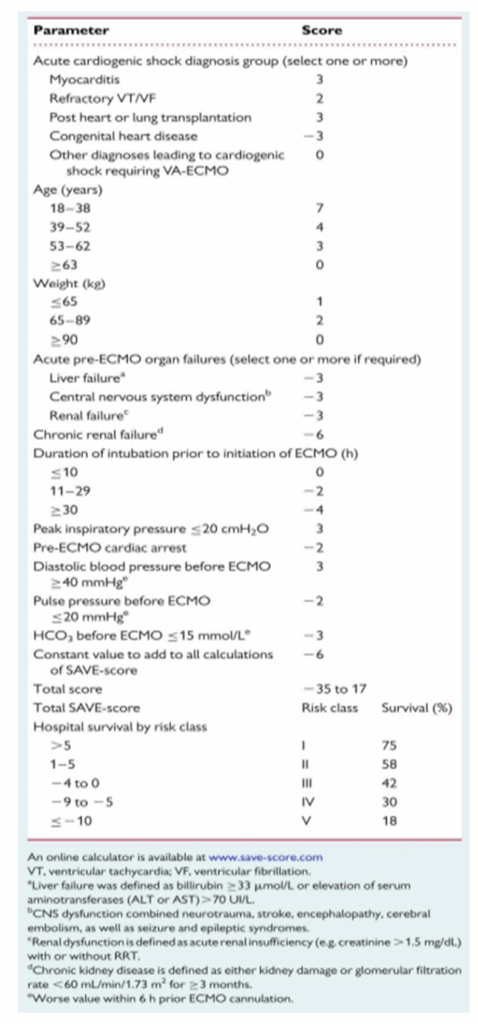
* reference : Mater Misericordiae University Hospital